Command Line Arguments
Usually we write main like this
void main()You’ll often see it written like this instead
int main(int argc, char* argv[])This allows us to give our program inputs/arguments. The second input, argv stores the name of the program and the values of the arguments while the first input tells us how many we received.
We give a program inputs on the command line by following the ./programName with the inputs. If we wanted to give the program three inputs, 5, 5.5 and the string “hello world” we could type:
./programName 5 5.5 "hello world" In this case argc==4 because there is one program and three arguments. argv is an array of strings (char* s) with the following values
argv[0] == programNameargv[1] == "5"argv[2] == "5.5"argv[3] == "hello world"
Note that the numeric inputs are stored as strings, not ints or floats. We can convert strings to numbers using the two functions
int atoi(char *s) // convert string to int
float atof(char *s) // convert string to floatEclipse
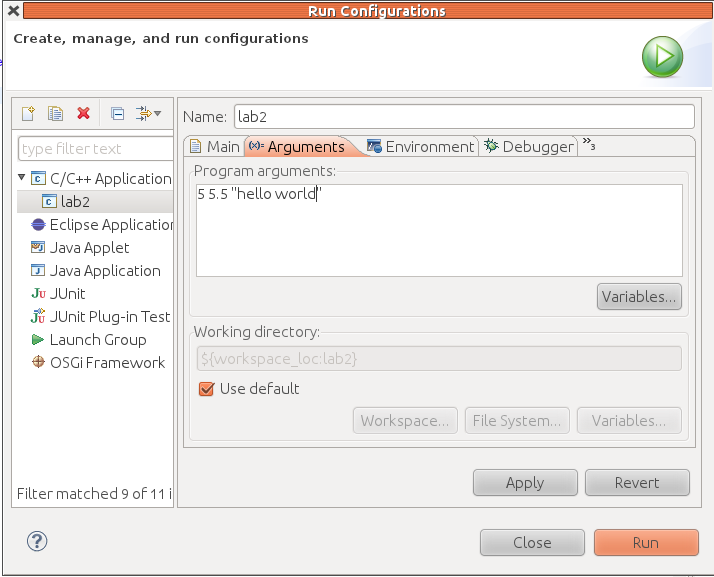
To enter arguments in Eclipse
- Right click on your project icon (in the left panel)
- Run As : Run Configurations…
- Click on the Arguments Tab
- Enter in just the arguments/inputs, not the program name